Why can black/green silicon carbide be used for make polishing discs?

The main reason for using silicon carbide in granite polishing discs is the physical and chemical properties of sic, which make it perform well in the polishing process.
First, silicon carbide has high hardness and wear resistance. The Mohs hardness of sic is as high as 9.2 to 9.5, second only to diamond and cubic boron nitride, which makes it perform well under pressure and friction, and can effectively remove materials from the surface of the stone while reducing the wear of the abrasive. During the polishing process, the high-hardness sic abrasive can maintain the sharpness of the edge, improve the grinding efficiency and processing quality.
Second, silicon carbide has good thermal conductivity. During the polishing process, a lot of heat is generated between the stone and the abrasive. If it cannot be dissipated in time, it may cause the stone to deform or generate thermal stress, affecting the quality of the product. Sic can effectively conduct the heat generated during the polishing process, keep the temperature of the polishing area stable, and avoid damage to the stone due to thermal stress.
In addition, the particle size distribution of silicon carbide is uniform and self-sharpening. The particle size distribution of sic abrasive is concentrated and uniform, and the abrasive grains are of equal area and have sharp edges, which enables it to maintain good self-sharpening during the polishing process, that is, the abrasive can continuously self-trim during the polishing process to maintain a sharp edge. This feature improves the polishing efficiency and processing quality, making the stone surface flatter and smoother.
Finally, silicon carbide has excellent chemical resistance. During the polishing process, the polishing material may react with the chemicals on the surface of the stone. Sic can resist the erosion of a variety of corrosive media, ensuring the stability and integrity of the material in a complex chemical environment.
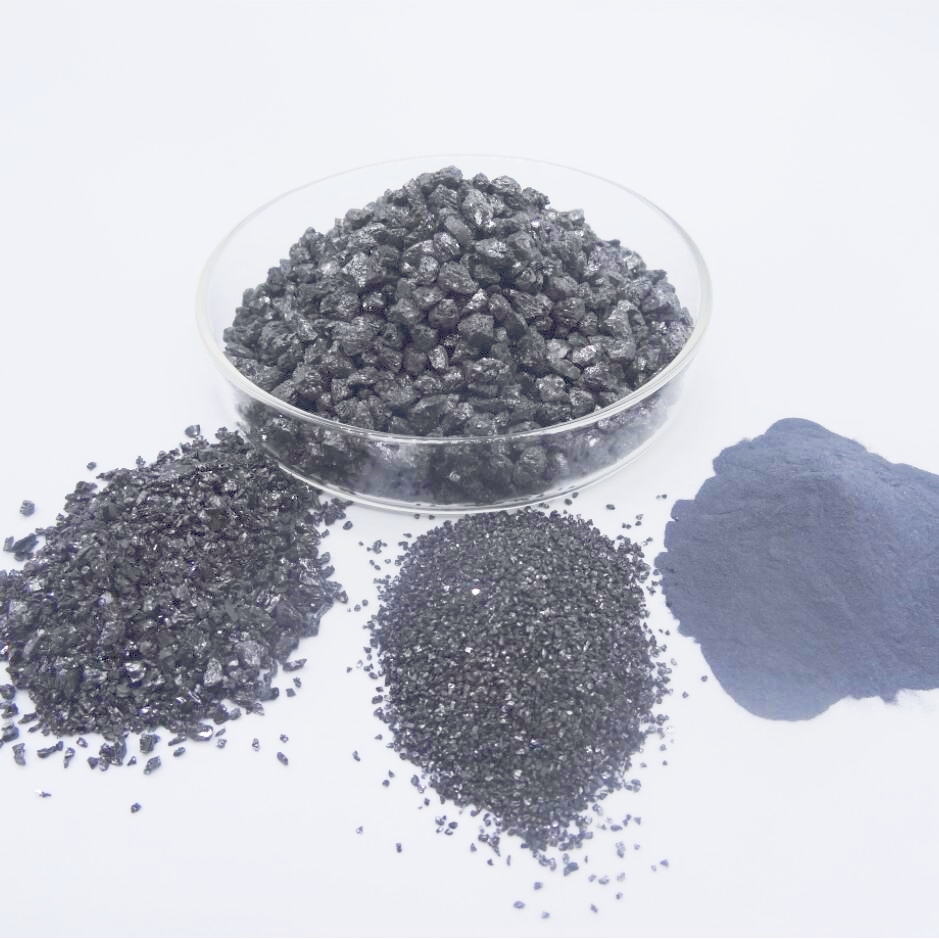
Black silicon carbide:
Black sic is produced by smelting quartz sand, petroleum coke (or coal coke), wood chips, and other raw materials in a resistance furnace. It appears as a black opaque body with hexagonal crystals and a Mohs hardness of 9.15. Second only to diamond and boron carbide, it possesses brittle and sharp properties with a certain degree of conductivity.

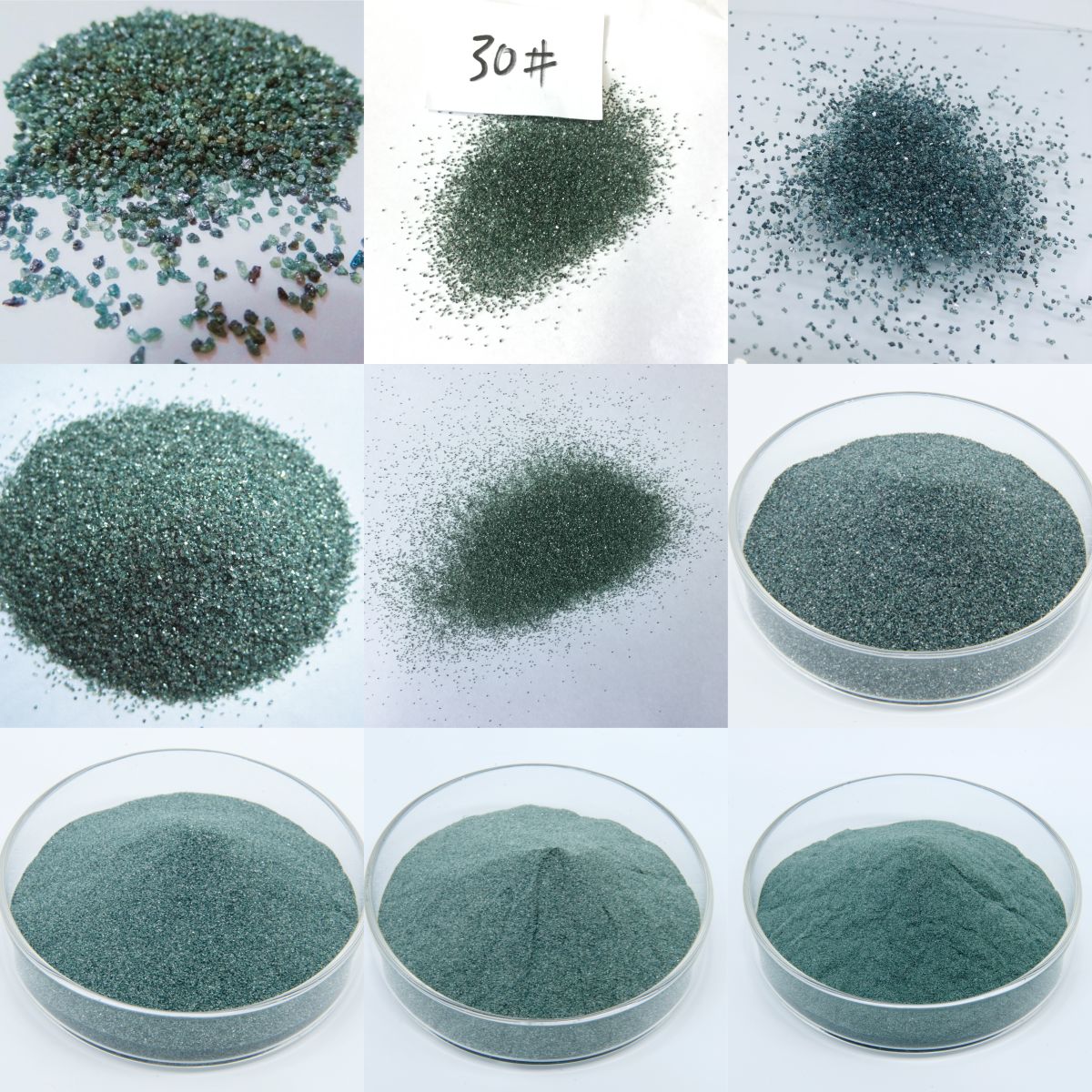
Green sic:
Green silicon carbide is a green translucent hexagonal non-metallic mineral product made from petroleum coke and high-quality silica as the main raw materials, with salt as an additive, and is produced through 2200° high-temperature smelting in a resistance furnace.
Data for green sic:
| Chemcial data | ||||
| SIC | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | F. Fe | C |
| 99%min | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 | 0.04% | 0.1% |
| Physical data | ||||
| colour | Mohs hardness | Knoop harnedd | Specific Gravity | Melting Point |
| green | 9 | 2600 | 3.2 g/cm3 | 2600° |
Green silicon carbide: